Beyond the buzz and hype about blockchain technology being revolutionary, the current state of enterprise application development using blockchain as a whole has not progressed beyond experimental phases.
There are two main reasons for this situation: one, enterprises being skeptical, have focused towards the various implementations of private or permissioned blockchains and second, the limited scalability provided by available blockchains.
And yet there are several options available to be used as enterprise blockchain, a number of them implementations of the Bitcoin protocol. Since most of these node implementations have altered the protocol’s fundamental capabilities, it’s essential for enterprises to gain a firm understanding of Bitcoin’s original protocol and built-in features.
Key principles of the Bitcoin protocol
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system which means that two parties can transact i.e. exchange value over the Internet, without involving a trusted intermediary.
It utilises cryptographic tools – digital signatures and hash functions to enable and record the exchange. (Contrary to common perception, actions inscribed to the Bitcoin record are not automatically encrypted, but published in plain text.)
Either the sender or the receiver of each transaction broadcasts it to the network of nodes / miners.
Within the network, all transactions that are broadcasted within a certain time frame are grouped together to form a ‘block’.
The staging area where miners pool these transactions broadcasted to the network is called a mempool.
The miners compete and cooperate with each other within the ecosystem. They compete with each other to verify the integrity of each transaction, received within a certain timeframe, and solve a hash puzzle using a technique similar to brute force. The miner who solves the hash puzzle first proposes the block to the network, as a candidate to be added as the next block in the blockchain, along with the proof-of-work.
Other miners co-operate by validating the proof-of-work and integrity of transactions, accepting it as a valid block in the chain. These validated transactions are grouped together as a block and the solution to the hash puzzle is recorded in the block header.
When the next block is mined, validated and accepted the block header of the previous block is referenced in the next block header. This process subsequently generates a chain of blocks. Though the data structure that evolves from the protocol implementation is as a blockchain, it is essentially a timestamp server or Timechain, which timestamps each block in a chronological order, and the timestamp for a block is attributed to each transaction that is part of that particular block. The transactions within a block are recorded in the chronological order and nodes implement the ‘first seen rule’ to overcome conflicts
The diagram below displays an example of payment settlement process which shows an exchange between two entities, Alice and Bob.
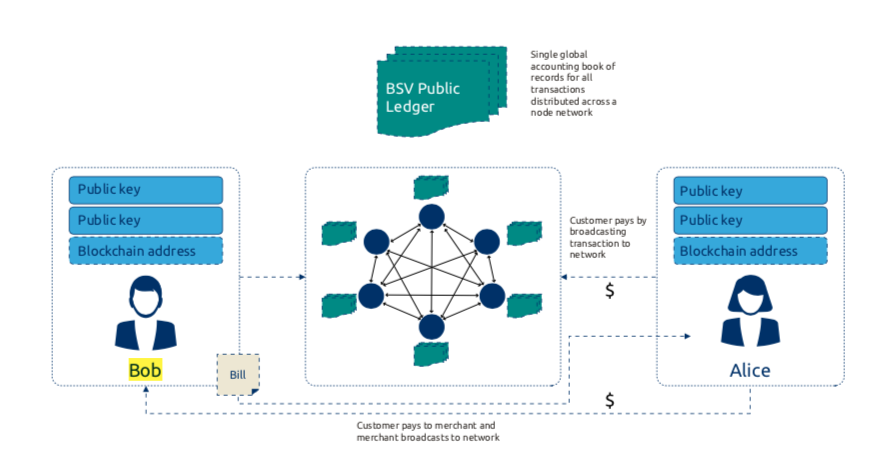
Applying the Bitcoin protocol to the digital economy to redefine trust, security and value exchange
In terminologies of artist and aesthetics there is a famous saying, ‘simple is hard’. The same principle applies to the core foundations of the Bitcoin blockchain.
With the evolution of the Internet, the current digital ecosystem is hampered by
- Increase in cost due to sophisticated security measures
- trusting the intermediaries and
- data and money operating separately
These aspects not only make building enterprise products a complex affair but have led to a saturation with respect to new business models.
Redefining Security
The lesser known fact about security is that security is about economics. Though counter-intuitive, it is simple to understand that ‘Criminal groups act as profit seeking enterprises, and the ability to shift the economic returns away from this activity results in a lower amount of crime’.
The network processors, a.k.a miners, abide by a centralised, stable, set in stone, protocol like the Internet and compete with each other to earn incentives. These incentives are aligned to the securing of the network. The larger the network grows, the more secure it becomes. For global enterprises, it means less cost on security.
Expanding the cost savings, the sheer nature of distributed, immutable, verifiable, auditable ledger can save huge amounts of operational costs on governance, compliance. With distributed global economy, organisations rely on data for decisions, flowing in from multiple data sources. The aspect of one global chain, having immutable data makes it trustworthy and reduces the friction between multiple parties giving enterprises visibility and one view of records.
Redefining Trust
The BSV blockchain shifts the paradigm of trust by providing capability to perform transactions peer-to-peer, in a transparent manner, which is not possible in the current ecosystem without involvement of central banks for payment processing and settlement, or third parties for audit, reputation, contract negotiations etc. The scalability and robustness of the system provides instinct transactions rather than relying on end of day settlements or batch processing. Not only this, micropayments which was never possible ever today, due to high transaction fees, is a game-changer. It augments the current customer base giving a strong strategic advantage to businesses.
Redefining value exchange through the unification of Bit and Coin
The Internet was built with the gap of keeping data and money as separate systems, which lead to organisations seeking profits from the privacy of users. It is one system that records events globally and immutably, making payments just a specific type of events and bridges the existing gap of monetising the data for a value as small as 1/100 of the cent.
Bitcoin as the name has both ‘bit’ and ‘coin’ i.e. data and money. Given data is the most important commodity in the current world, the BSV blockchain revolutionises the way this commodity is traded.
Built on the strong foundation of scalability, stability, security and instant transactions, the BSV blockchain promises to be the right choice for enterprises. It revolutionises not only the business models but also safeguards the enterprises for reputation by providing them fraud proof capabilities.
eBook: Enterprise blockchain products using the BSV blockchain
To learn more about the properties of the Bitcoin protocol, how the BSV blockchain’s implementation distinguishes it from other enterprise-scale blockchains and the applications and products that can be built using BSV blockchain, download our new eBook.
