AI in litigation is transforming the legal landscape by introducing innovative tools and techniques, such as machine learning, that enhance efficiency and accuracy. This shift towards AI legal technology offers numerous benefits for both lawyers and their clients.
Key Innovations and Applications in Jury Selection
AI-Powered Techniques for Bias Detection: Advanced algorithms can identify potential biases in the jury selection process by analyzing various factors, such as demographic information, historical jury decisions, and case-specific details. This promotes fairness and impartiality by ensuring that prejudiced perspectives do not influence the trial outcome.
Demographic and Historical Analysis for Diverse Jury Selection: By utilizing AI to analyze demographic data and historical jury outcomes, lawyers can ensure the selection of a diverse and balanced jury. This approach not only enhances the representativeness of the jury but also strengthens the overall integrity of the judicial process.
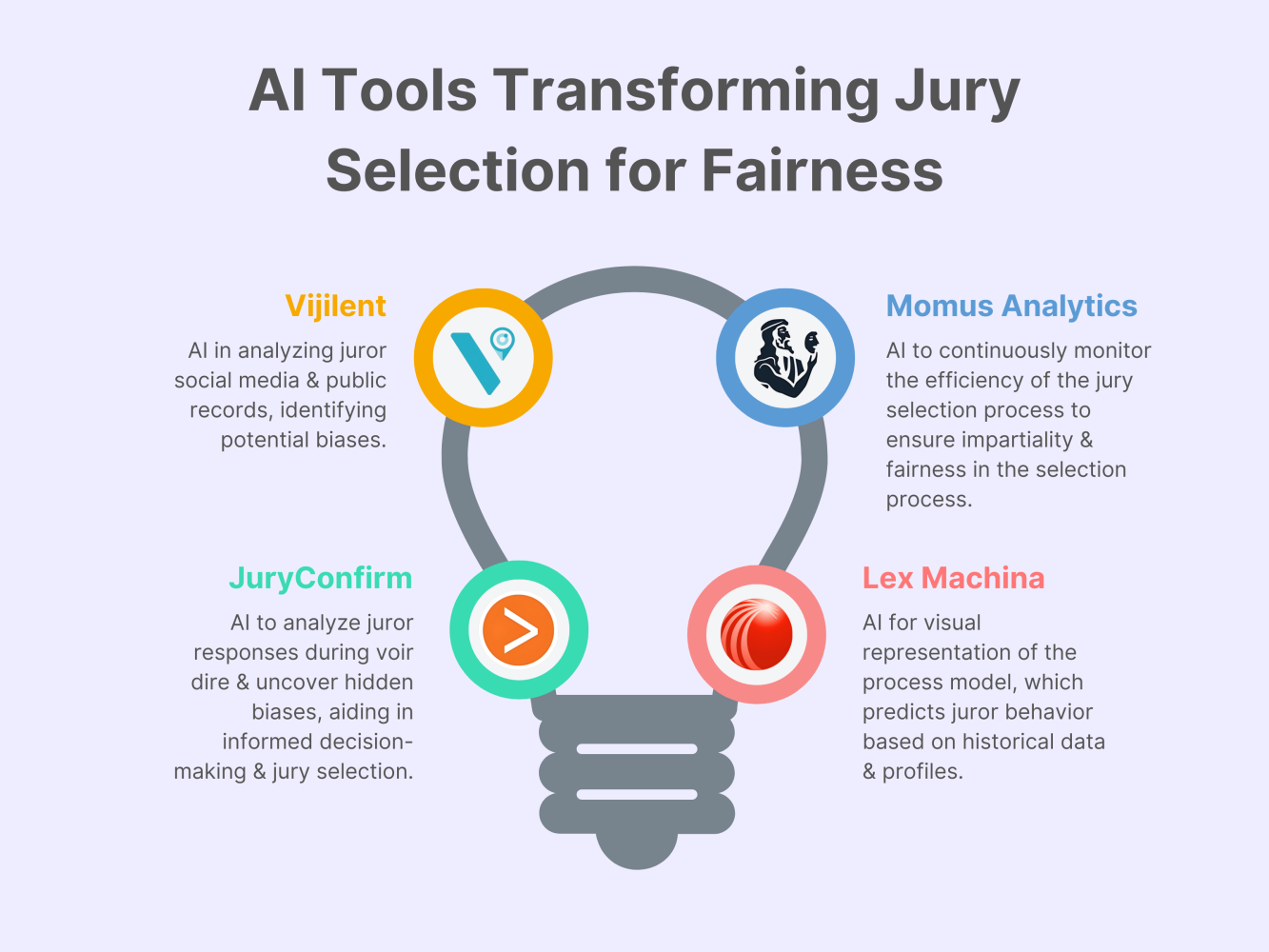
The infographic highlights the role of innovative AI tools in enhancing the jury selection process. These advanced AI applications collectively work to create a more balanced and impartial jury, significantly improving the integrity of the legal process.
Reveal by Vijilent: This AI-powered tool helps identify potential biases in the jury selection process by analyzing juror social media activity and public records. By providing insights into juror backgrounds, Reveal promotes fairness and impartiality in jury selection, ensuring a more balanced and objective jury.
Momus Analytics: Using predictive analytics, Momus Analytics evaluates potential jurors’ tendencies and biases based on their demographic information and historical behavior. This allows lawyers to make informed decisions about which jurors are most likely to be impartial and fair, thereby improving the overall integrity of the trial.
JuryConfirm & Evidence Analyzer by Magna Legal Services: JuryConfirm utilizes AI to analyze juror responses during voir dire, identifying hidden biases and attitudes that may not be apparent through traditional questioning. The Evidence Analyzer further assists by evaluating the strength and weaknesses of evidence from the perspective of different juror profiles, helping lawyers tailor their strategies to better appeal to a diverse jury.
Lex Machina by LexisNexis: This platform leverages big data and machine learning to predict juror behavior based on historical case outcomes and juror profiles. Lex Machina provides insights into how different types of jurors have decided similar cases in the past, enabling lawyers to make more strategic decisions during jury selection.
In this article, we take a closer look into the groundbreaking advancements that are redefining the landscape of litigation. We emphasize the critical importance of fairness and impartiality in AI-powered jury selection, and examine how these innovative technologies are revolutionizing legal practices and shaping the future of law.
Ensuring Fairness and Impartiality in AI Jury Selection
AI jury selection is a rapidly growing field in litigation technology. It uses advanced data analysis methods to improve the process of selecting jurors. By employing tools powered by artificial intelligence (AI), legal professionals can identify potential biases and make better decisions when choosing jurors.
How AI Helps in Jury Selection
AI techniques simplify the jury selection process by analyzing large amounts of data to assess potential jurors. These tools use machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to:
Analyze Demographic Data: AI systems go through demographic information to ensure a diverse and representative pool of potential jurors. By considering factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, AI helps create a jury that reflects the community’s makeup.
Evaluate Social Media Activity: The social media profiles of potential jurors are examined for any biases or prejudices that could impact their judgment. AI scans posts, likes, shares, and comments to detect patterns indicating partiality, ensuring that jurors selected are impartial and fair.
Predict Juror Behavior: By studying past cases and juror behavior, AI can forecast how certain individuals might react to specific types of evidence or arguments. This predictive capability allows lawyers to develop strategies that align with the likely perspectives of the jurors.
Review Public Records: AI tools can sift through various public records, such as property ownership, financial history, and previous legal encounters, to identify potential biases or conflicts of interest. This comprehensive analysis helps in selecting jurors who are impartial and suitable for the case.
The Role of Data Analysis in Detecting Biases
Data analysis plays a crucial role in identifying biases that may not be immediately apparent during traditional jury selection methods. AI-powered systems analyze patterns that suggest bias, enhancing the fairness and impartiality of the legal process. Key areas of focus include:
Historical Voting Records: AI analyzes past voting patterns to reveal political leanings that might influence a juror’s impartiality. By examining this historical data, AI can highlight trends and preferences, suggesting how a juror might view certain legal issues or parties involved in a case.
Employment History: Certain professions may have inherent biases based on industry norms and practices. For instance, individuals working in law enforcement might have different perspectives compared to those in social work. AI can analyze employment records to detect such biases, helping lawyers understand potential predispositions that could affect juror decisions.
Community Involvement: Membership in specific organizations or active participation in community events can indicate potential biases. For example, involvement in advocacy groups or political organizations can provide insights into a juror’s values and beliefs. AI systems can scan for these affiliations and assess their potential impact on juror impartiality.
Educational Background: The level and field of education can influence a person’s worldview and biases. AI can analyze educational history to determine if a juror’s academic experiences might sway their perspective on certain issues. For example, a background in criminal justice might affect views on law enforcement and legal proceedings, while a degree in social sciences could indicate different biases.
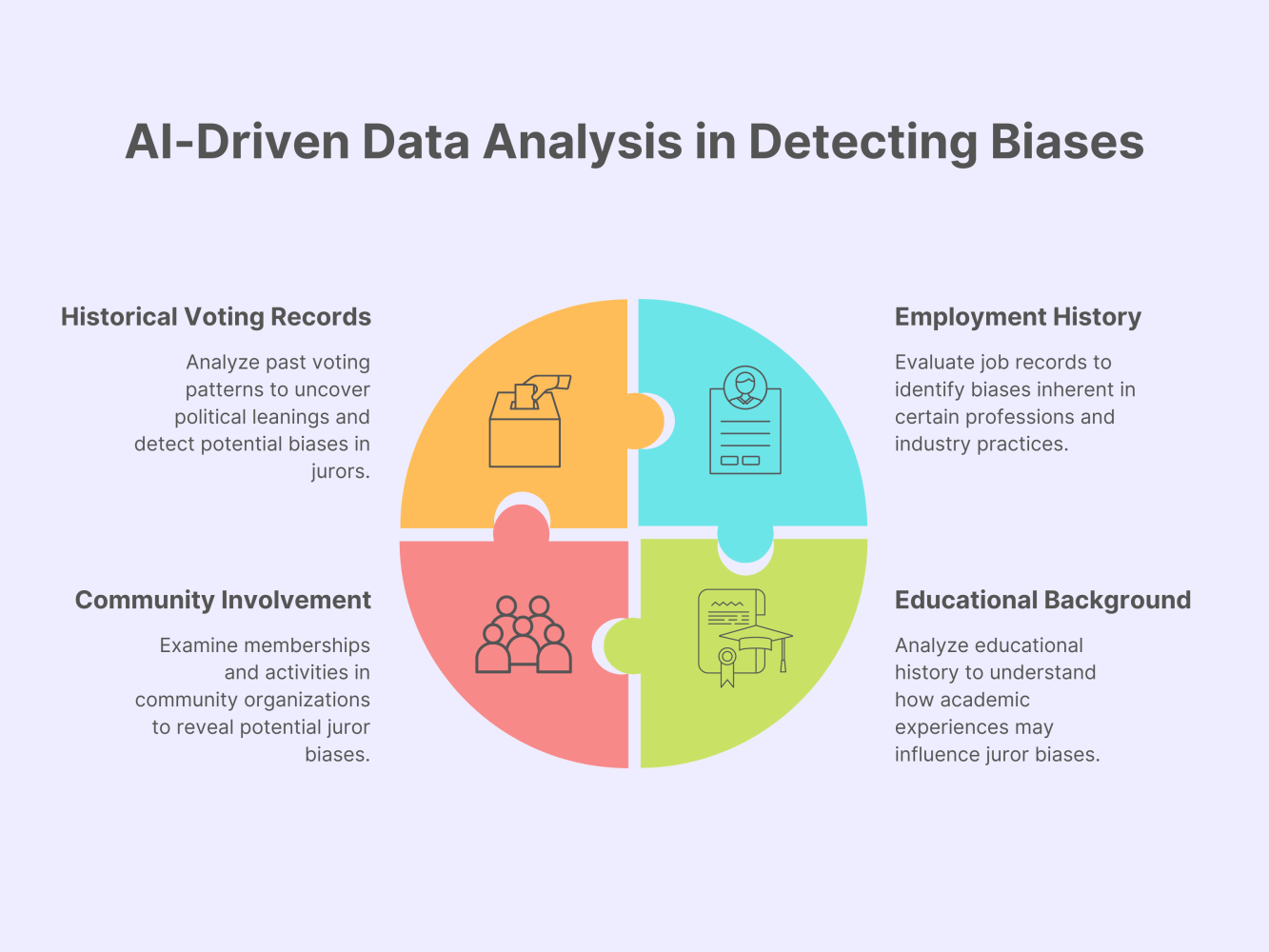
The visual representation above illustrates how AI-driven data analysis plays a crucial role in detecting biases in jury selection. This comprehensive approach ensures a more impartial and fair jury selection process, ultimately enhancing the integrity of the legal system.
Challenges in Balancing Technological Efficiency and Constitutional Rights
While AI offers significant advantages in the legal sector, it also presents challenges in balancing efficiency with constitutional rights. The right to an impartial jury is enshrined in the Sixth Amendment, making it imperative that AI applications do not infringe upon this fundamental right.
Key Challenges
Algorithmic Transparency: Ensuring AI algorithms are transparent and understandable is critical. Black-box algorithms can lead to decisions that are difficult to scrutinize or contest. The complexity of these algorithms can obscure decision-making processes, raising concerns about fairness and accountability.
Solution: Implementing Explainable AI (XAI) techniques helps clarify how decisions are made by these systems. XAI provides insights into the reasoning behind AI-driven decisions, making it easier for legal professionals to understand, trust, and contest AI findings if necessary. This approach fosters greater transparency and accountability in AI applications.
Bias in Training Data: AI systems learn from historical data, which may contain inherent biases. If not addressed, these biases can perpetuate existing inequalities and lead to unjust outcomes in jury selection. Historical data might reflect societal biases, such as racial, gender, or socioeconomic prejudices, which can be inadvertently encoded into AI models.
Solution: Regular audits and updates of training datasets ensure they reflect current societal norms and values. By continuously refining and correcting the data, AI systems can be trained to recognize and mitigate biases, promoting fairness and impartiality in the jury selection process. Additionally, diverse and representative datasets should be used to train AI models to minimize the risk of bias.
Legal Precedent and Acceptance: The legal system must adapt to accept AI-generated insights without compromising legal standards. Integrating AI into legal processes requires overcoming skepticism and resistance from legal professionals who may be wary of relying on technology for critical decisions.
Solution: Establishing clear guidelines and regulatory frameworks that govern the use of AI in jury selection can help build trust and ensure compliance with legal standards. These frameworks should define the ethical and legal boundaries of AI use, providing a structured approach for integrating AI into the judicial process. Education and training for legal professionals on the benefits and limitations of AI can also facilitate its acceptance and proper utilization.
Balancing the benefits of AI with the need to uphold constitutional rights requires ongoing effort and vigilance. By addressing these challenges, the legal system can harness the power of AI to enhance efficiency while ensuring fairness and justice in the jury selection process.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations also play a significant role in the adoption of AI for jury selection. These considerations ensure that the implementation of AI technologies aligns with legal and moral standards, preserving the integrity of the judicial process.
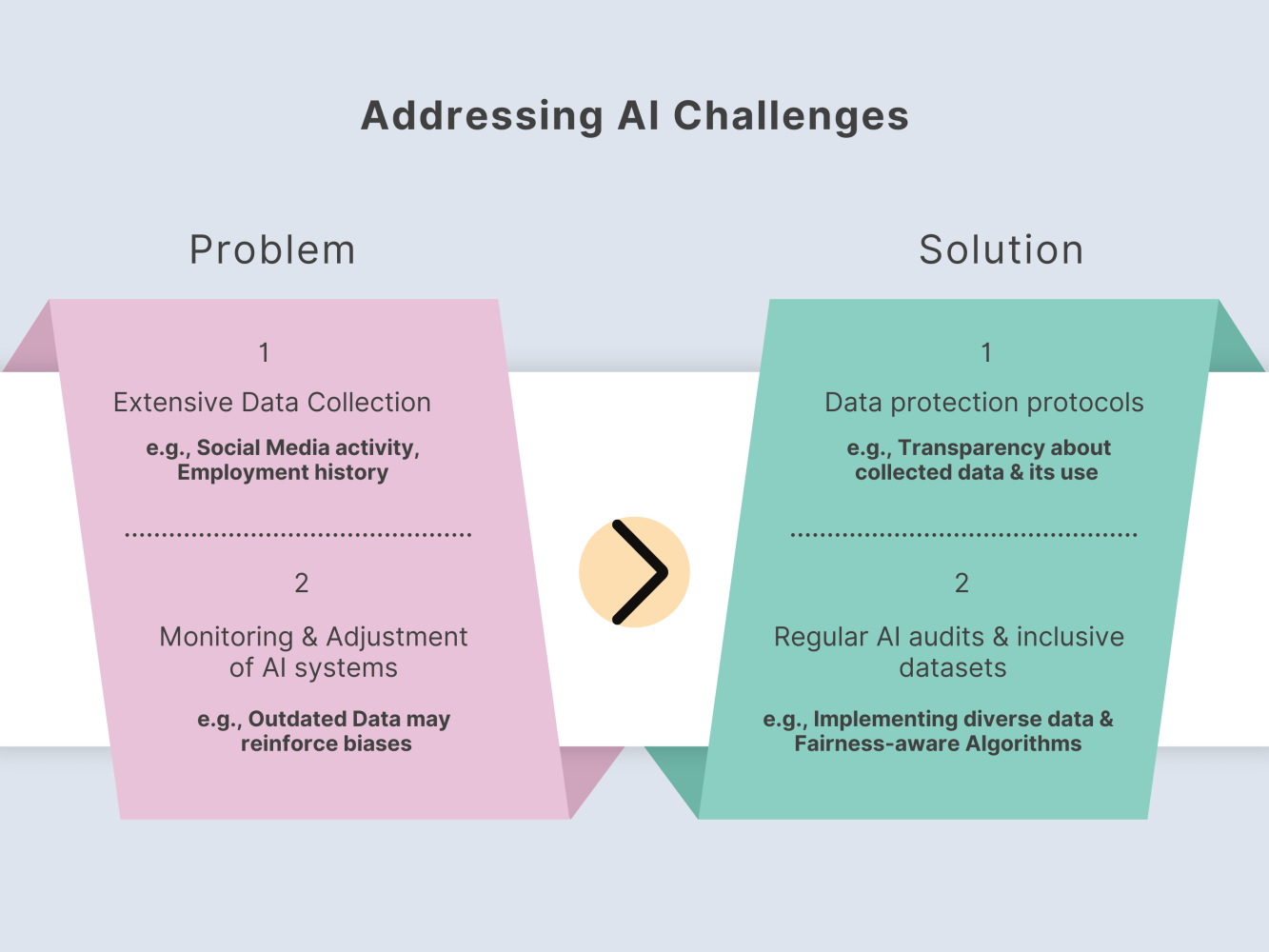
The graphic above highlights key challenges in AI-driven jury selection, such as extensive data collection and bias in AI systems. It also presents effective solutions, including implementing data protection protocols and conducting regular AI audits. These measures ensure transparency, privacy, and fairness in the jury selection process.
Privacy Concerns: Extensive data collection might infringe on potential jurors’ privacy rights. AI systems often require access to a wide range of personal information, including social media activity, employment history, and other sensitive data. This level of scrutiny can lead to concerns about the invasion of privacy and the misuse of personal information.
Solution: Implementing robust data protection protocols and ensuring that data collection practices comply with privacy laws and regulations is crucial. Transparency about what data is collected and how it is used can also help mitigate privacy concerns and build trust among potential jurors.
Fairness: Ensuring that all demographic groups are fairly represented requires constant monitoring and adjustment of AI systems. AI algorithms must be designed and trained to avoid perpetuating existing biases and to ensure that jurors are selected in a manner that reflects the diversity of the community.
Solution: Regular audits of AI systems and their outcomes are necessary to identify and correct any biases that may arise. Developing inclusive datasets and continuously refining algorithms to promote fairness can help achieve a balanced representation of all demographic groups in the jury selection process.
Future Prospects
Advancements in AI will continue to refine the jury selection process, making it more unbiased and equitable. Ongoing improvements in algorithmic fairness and transparency will render these tools indispensable for legal professionals.
Integrating AI technologies thoughtfully and ethically allows the legal system to leverage their strengths while safeguarding fundamental rights. This balanced approach promises a more just litigation process, upholding both technological efficiency and constitutional principles. As AI evolves, its role in the legal sector is set to expand, offering new opportunities to enhance fairness and efficiency in various judicial aspects.
Enhanced Predictive Accuracy: Future AI advancements will likely focus on improving the predictive accuracy of juror behavior. This will allow for more precise assessments of potential biases and tendencies, enabling legal teams to make better-informed decisions during jury selection.
Greater Transparency and Accountability: The development of more transparent and accountable AI systems will ensure that decisions made by these technologies can be easily understood and challenged if necessary. This transparency will enhance trust in AI-driven jury selection processes, ensuring they are subject to appropriate scrutiny.
Integration with Broader Legal Technologies: As AI tools for jury selection become more sophisticated, they will likely integrate with other legal technologies, such as case management systems and evidence analysis tools. This integration will streamline legal workflows and further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the legal process.
Conclusion
Overall, the thoughtful and ethical adoption of AI in jury selection has the potential to transform the judicial system, making it fairer, more efficient, and more representative of the community. By continuously addressing ethical considerations and leveraging technological advancements, the legal system can ensure that AI-driven jury selection upholds the highest standards of justice.
