AI is revolutionizing litigation by introducing advanced tools and techniques that enhance efficiency and accuracy. The integration of AI in legal processes provides significant benefits for both lawyers and their clients.
Key Innovations and Applications in Courtroom Analytics
Data-Driven Trial Presentations: AI enables lawyers to create compelling trial presentations by analyzing data from previous court cases. This data-backed approach strengthens the evidence presented in court.
Predictive Insights: Using insights from past case outcomes, AI helps predict future trends and develop effective legal strategies, making litigation more strategic and informed.
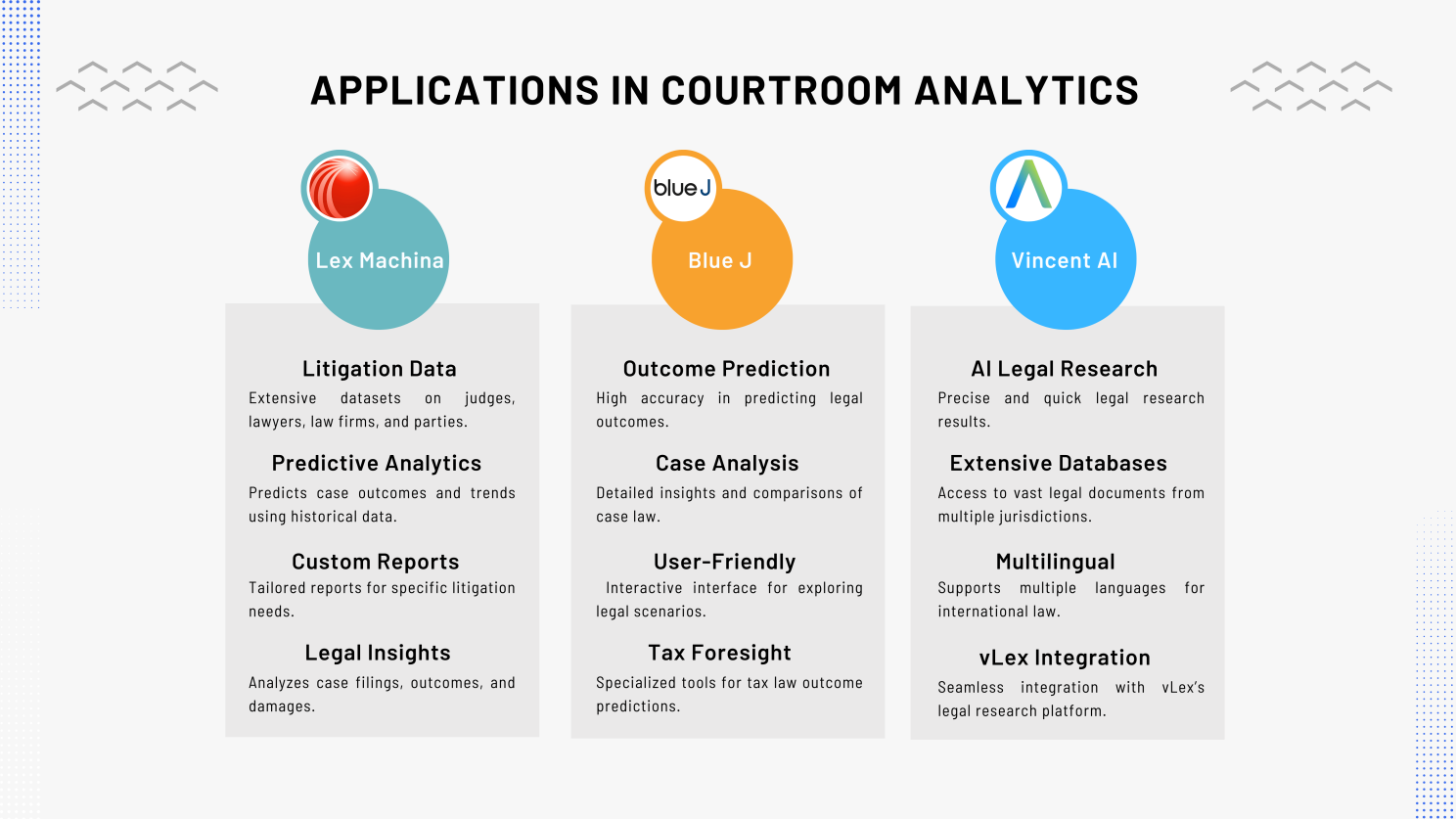
1. Lex Machina by LexisNexis: Provides comprehensive courtroom analytics and predictive insights to aid legal professionals in making data-driven decisions. 2. Blue J Legal: Utilizes AI to predict legal outcomes with high accuracy, helping lawyers understand how past cases might influence current ones. 3. Vincent AI by vLex: Offers powerful AI-driven legal research and analytics, enabling lawyers to access relevant case information quickly and efficiently.
In our new article we dive deeper into the pivotal advancements redefining the landscape of litigation focussing on predictive and courtroom analytics in law. We examine how these technologies are revolutionizing legal practices and their implications for the future.
How Predictive Analytics Law is Used to Determine Case Outcomes
The Emergence of Predictive Analytics Law
The emergence of predictive analytics law has revolutionized the way lawyers approach case outcomes. This innovative approach involves leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze extensive legal data sets and make accurate predictions based on that information.
Key Features of Predictive Analytics in Law
Data Analysis: By analyzing vast amounts of legal data, predictive analytics can identify trends and patterns that might not be immediately obvious. This includes:
- Historical case outcomes
- Judicial behavior
- Settlement amounts
Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms are trained to recognize specific patterns within the data. They undergo a rigorous training process that includes:
- Supervised Learning: Using labeled data to teach the algorithm how to make decisions.
- Unsupervised Learning: Allowing the algorithm to find hidden patterns without explicit instructions.
Accurate Predictions: Once trained, these algorithms can make highly accurate predictions about various aspects of a case, such as:
- Likelihood of winning or losing
- Potential settlement ranges
- Optimal legal strategies
Benefits for Legal Professionals
Predictive analytics offers several advantages for legal professionals:
- Efficiency: Reduces the time spent on research and analysis.
- Cost-effectiveness: Minimizes the need for extensive manual labor.
- Strategic Planning: Helps lawyers develop more effective strategies based on data-driven insights.
Applications in Legal Practice
Predictive analytics can be applied in various areas within the legal field:
- Litigation Forecasting: Predicts the outcome of court cases, helping lawyers decide whether to settle or proceed to trial.
- Contract Analysis: Assesses potential risks and compliance issues in contractual agreements.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Evaluates potential risks and benefits to inform decision-making processes.
By incorporating predictive analytics, law professionals can navigate complex legal landscapes with greater confidence and precision.
The Role of Predictive Analytics in the Legal Field
Predictive Analytics in Law
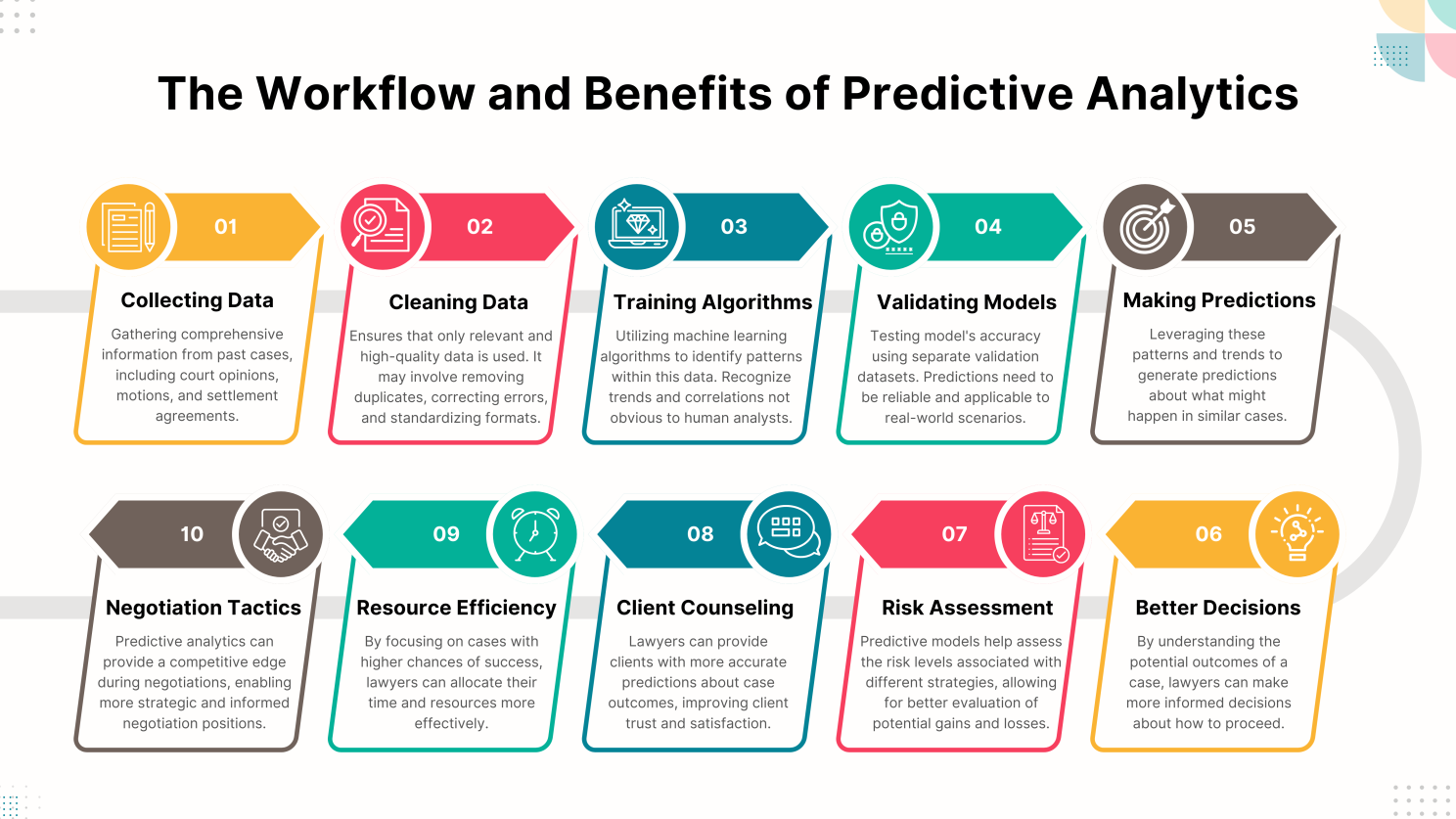
Predictive analytics in law leverages historical case data to forecast possible outcomes for new cases, enhancing decision-making and strategy formulation. The first row of the infographic (Infographic steps 01-05) details the essential steps in the predictive analytics workflow, including collecting data, cleaning data, training algorithms, validating models, and making predictions. Each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and effectiveness of predictive analytics in legal applications.
The process starts with (01) gathering extensive information from past cases, including court opinions, motions, settlement agreements, and metadata such as judge rulings and jury decisions. This raw data often contains irrelevant information or errors, so it undergoes (02) cleaning and preprocessing to ensure only high-quality data is used. Next, (03) machine learning algorithms are trained on this refined data. The accuracy of these algorithms is then validated (04) using a separate dataset to ensure their predictions are reliable and applicable in real-world scenarios. Once validated, these models generate predictions (05) about potential verdicts, estimated settlements, and the likelihood of case dismissals, among other outcomes.
The system continuously learns and updates with new data from ongoing cases, enhancing its predictive accuracy over time. This continuous learning process makes the model more robust and reliable for future predictions.
Predictive analytics provides significant benefits for legal professionals (Infographic steps 06-10).
By enabling (06) more informed decision-making and (07) comprehensive risk assessment. Lawyers can use these models to predict the outcomes of cases, helping them determine the best strategies to pursue. This technology also enhances client relationships by providing more accurate forecasts, thereby improving client satisfaction and trust (08). Additionally, predictive analytics allows for (09) efficient resource management, directing efforts towards cases with higher success probabilities and reducing overall costs. Data-driven insights help develop robust litigation strategies and recognize patterns from past cases, enabling anticipation of opposing counsel’s actions. This comparative analysis also aids in setting realistic benchmarks and tracking progress in litigation. Furthermore, it enhances (10) negotiation tactics and provides valuable insights into likely settlement amounts, aiding in strategic negotiations. Understanding an opponent’s behavior based on historical data allows for tailored negotiation approaches, increasing the likelihood of favorable outcomes.
Tools like Lex Machina exemplify the use of predictive analytics in law, providing insights into past judicial rulings to help lawyers tailor their strategies accordingly. These steps collectively offer powerful tools for navigating the complexities of legal cases more effectively.
Considering Ethics and Fairness in Predictive Analytics
While there are clear benefits to using predictive analytics in the legal field, it’s crucial to address ethical concerns:
Bias in Data: Machine learning algorithms heavily rely on the quality and fairness of the data they’re trained on. If historical data contains biases, such as discrimination against certain groups, then the algorithm may also produce biased results.
For example, if past data shows a bias against a particular demographic, the algorithm may unfairly predict unfavorable outcomes for similar demographics in future cases.
Transparency: Understanding how algorithms arrive at their conclusions is crucial for trust and accountability. Unfortunately, many AI systems operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to see why a certain prediction was made.
“The ‘black box’ nature of many AI systems makes it difficult to understand and explain their decision-making processes.” says Sandip Patel KC in Quantum Resilience.
Accountability: Determining responsibility when an AI-driven prediction influences a legal decision is a complex issue that needs to be resolved.
How to Address Ethical Challenges in Predictive Analytics
To tackle these challenges and ensure fairness in the use of predictive analytics:
Reducing Bias:
- Re-Sampling: Adjusting the dataset to have a more balanced representation of different groups.
- Re-Weighting: Assigning different weights to data points to counteract inherent biases. This technique ensures that underrepresented groups are adequately considered in the algorithm’s training process.
- Regular Audits: Periodically auditing the datasets and algorithms to identify and rectify any emerging biases.
Increasing Transparency:
- Explainable AI (XAI): Developing AI models that can provide clear, understandable explanations for their decisions. This helps stakeholders trust and understand the reasoning behind predictions.
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of how datasets are curated, how algorithms are trained, and any changes made over time. This practice fosters accountability and makes it easier to trace decision-making processes.
- Open Source Models: Encouraging the use of open-source AI models where possible, allowing independent verification and community-driven improvements.
Maintaining Human Oversight:
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Systems: Integrating human judgment into AI decision-making processes to validate and interpret predictions before they influence final decisions.
- Ethical Committees: Establishing committees to oversee AI deployments, ensuring they adhere to ethical standards and industry best practices.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing systems for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of AI performance, ensuring that any deviations from expected behavior are promptly addressed.
These steps collectively contribute to a more fair, transparent, and accountable use of predictive analytics in legal contexts.
The Power of Courtroom Analytics in Trial Presentations
Courtroom analytics is transforming the way trial presentations are prepared and delivered. By leveraging data from courtroom proceedings, legal professionals can create more compelling and persuasive cases.
Leveraging Data for Persuasive Trial Presentations
Analytics tools allow lawyers to:
- Analyze past case outcomes: Understanding how similar cases were decided helps in crafting strategies that align with historical data.
- Monitor real-time courtroom dynamics: Tools like transcription services provide instantaneous access to spoken words, enabling quick adjustments and responses.
- Identify patterns in judicial behavior: Recognizing a judge’s tendencies or preferences can influence how arguments are framed.
This data-driven approach ensures that trial presentations are not only well-informed but also strategically tailored to increase the chances of favorable outcomes.
Practical Use Cases of Electronic Courtroom Automation
Electronic courtroom automation streamlines numerous aspects of trial proceedings. Some notable applications include:
- Real-time evidence presentation systems: These systems facilitate the immediate display of documents, images, and videos, ensuring that evidence is presented clearly and efficiently. For example, a lawyer can instantly pull up a relevant contract clause during cross-examination.
- Automated transcription services: Transcriptions generated in real-time allow attorneys to keep track of everything said during the trial without missing any details. This is particularly useful for referencing previous statements or ensuring consistency in testimonies.
Enhancing Efficiency with Real-Time Tools
The integration of real-time tools enhances overall efficiency:
- Immediate document retrieval: Lawyers no longer need to sift through physical files; digital systems enable quick access to necessary documents.
- Interactive exhibits: Dynamic exhibits can be manipulated during the presentation to highlight specific points, making arguments more vivid and understandable.
Case Study: Impact on High-Stakes Litigation
In high-stakes litigation, where every detail counts, courtroom analytics provide an edge:
1. Complex financial disputes: Real-time data visualization tools can simplify intricate financial information, making it accessible to juries who may not have specialized knowledge. 2. Patent infringement cases: Automated systems can quickly cross-reference patent claims with existing patents, identifying potential conflicts or supporting evidence.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, the use of courtroom analytics is not without challenges:
- Data Security: Ensuring that sensitive information remains secure is paramount. Legal teams must implement robust cybersecurity measures.
- Cost: Initial setup and maintenance of these systems can be expensive. Balancing cost against benefits requires careful consideration.
Future Prospects for Courtroom Analytics
The future holds exciting prospects for courtroom analytics:
- AI-enhanced transcription: With advancements in AI, transcriptions will become even more accurate and context-aware.
- Predictive analysis integration: Combining predictive analytics with real-time data could provide deeper insights into trial progress and potential outcomes.
- Courtroom analytics represents a significant step towards smarter litigation practices by making trial presentations more precise and impactful.
Conclusion
Predictive analytics has significantly enhanced the way legal professionals determine case outcomes. By utilizing historical data and advanced algorithms, lawyers can now make more informed decisions, assess risks more accurately, and develop stronger litigation strategies. This data-driven approach not only improves the efficiency and effectiveness of legal practices but also boosts client satisfaction through precise predictions and better resource management. Predictive analytics enables lawyers to automate routine tasks, identify patterns in vast datasets, and anticipate opposing counsel’s moves, ultimately leading to more successful case outcomes.
